New publications as April 6th, 2015
PUBLICATIONS UP TO APRIL 6TH 2015
| 1. | Acta Ophthalmol. 2015 Apr 2. doi: 10.1111/aos.12710. [Epub ahead of print]
Author information:
Abstract
The use of blood derivatives represents an alternative therapeutic approach that is gaining interest in regenerative medicine due to its potential to stimulate and accelerate tissue healing. Autologous serum eye drops and platelet-enriched plasma eye drops are being used in the treatment of different ophthalmological disorders. In this review, we summarize the different blood-derived formulations used in the treatment and care of ocular surface disorders. The biological basis and use of autologous serum and plasma rich in growth factors are deeply evaluated as well as the challenges to be addressed in the future in this new generation of blood-derived therapies. © 2015 Acta Ophthalmologica Scandinavica Foundation. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd. |
| PMID: 25832910 [PubMed - as supplied by publisher] | |
| Related citations | |
 |
| 2. | Korean J Ophthalmol. 2015 Apr;29(2):131-7. doi: 10.3341/kjo.2015.29.2.131. Epub 2015 Mar 17.
Author information:
Abstract
PURPOSE:
To investigate the therapeutic effects of mineral oil (MO) and hyaluronic acid (HA) mixture eye drops on the tear film and ocular surface in a mouse model of experimental dry eye (EDE). METHODS:
Eye drops consisting of 0.1% HA alone or mixed with 0.1%, 0.5%, or 5.0% MO were applied to desiccating stress-induced murine dry eyes. Tear volume, corneal irregularity score, tear film break-up time (TBUT), and corneal fluorescein staining scores were measured at 5 and 10 days after treatment. Ten days after treatment, goblet cells in the conjunctiva were counted after Periodic acid-Schiff staining. RESULTS:
There was no significant difference in the tear volume between desiccating stress-induced groups. The corneal irregularity score was lower in the 0.5% MO group compared with the EDE and HA groups. The 0.5% and 5.0% MO groups showed a significant improvement in TBUT compared with the EDE group. Mice treated with 0.1% and 0.5% MO mixture eye drops showed a significant improvement in fluorescein staining scores compared with the EDE group and the HA group. The conjunctival goblet cell count was higher in the 0.5% MO group compared with the EDE group and HA group. CONCLUSIONS:
The MO and HA mixture eye drops had a beneficial effect on the tear films and ocular surface of murine dry eye. The application of 0.5% MO and 0.1% HA mixture eye drops could improve corneal irregularity, the corneal fluorescein staining score, and conjunctival goblet cell count compared with 0.1% HA eye drops in the treatment of EDE. |
| PMID: 25829831 [PubMed - in process] | |
| Related citations | |
  |
| 3. | Cornea. 2015 May;34(5):506-11. doi: 10.1097/ICO.0000000000000395.
Author information:
Abstract
PURPOSE:
To study the outcomes of cataract surgery in patients with graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). METHODS:
Retrospective review of 72 eyes of 41 patients (age, 17-69 years at the time of surgery) with chronic GVHD after HSCT, who underwent cataract surgery between 2008 and 2012 at the Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences, W. K. Kellogg Eye Center, University of Michigan. Ophthalmic data collected included best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA), responses to Ocular Surface Disease Index (OSDI) questionnaire, dry eye severity, and postoperative complications. RESULTS:
BCVA improved from 20/49 to 20/25 (P < 0.0001) after surgery. Eight patients (20%) had pretransplantation total body irradiation and 39 patients (95%) received systemic corticosteroids for the treatment of GVHD. Postoperative complications included cystoid macular edema (4 eyes), corneal ulceration with perforation (2 eyes: 1 infected and 1 sterile), and band keratopathy (1 eye). After surgery, subjective OSDI responses and dry eye disease (DED) did not change significantly from before cataract surgery, although OSDI showed a trend toward worsening. CONCLUSIONS:
With careful monitoring and management of DED and concurrent ocular surface disease, cataract surgery generally has good visual outcomes in patients with GVHD. However, aggravation of the preexisting ocular surface disease is frequent, and despite meticulous postoperative maintenance therapy, vision-threatening complications may occur. |
| PMID: 25826324 [PubMed - in process] | |
| Related citations | |
 |
| 4. | Cornea. 2015 May;34(5):491-6. doi: 10.1097/ICO.0000000000000379.
Author information:
Abstract
PURPOSE:
Standard therapies for severe dry eye are limited and fail to resolve the problem. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the safety and efficacy of Thymosin β4 eye drops (RGN-259) as a novel therapy for severe dry eye disease (including that associated with graft vs. host disease). METHODS:
A small, multicenter, randomized, double-masked, placebo-controlled 56-day phase 2 clinical trial including a 28-day follow-up at 2 US sites. Nine patients with severe dry eye were treated with either RGN-259 (0.1%) or vehicle control 6 times daily over a period of 28 days. Dry eye sign and symptom assessments, such as ocular discomfort (using the OSDI questionnaire) and corneal fluorescein staining (using the NEI workshop grading system), were evaluated at various time points. RESULTS:
Statistically significant differences in both symptom and sign assessments, were seen at various time points throughout the study. Of particular note at day 56, the RGN-259-treated group (12 eyes) had 35.1% reduction of ocular discomfort compared with vehicle control (6 eyes) (P = 0.0141), and 59.1% reduction of total corneal fluorescein staining compared with vehicle control (P = 0.0108). Other improvements seen in the RGN-259-treated patients included tear film breakup time and increased tear volume production. CONCLUSIONS:
In this small trial, RGN-259 eye drops were safe and well tolerated and met key efficacy objectives with statistically significant symptom and sign improvements, compared with vehicle control, at various time intervals, including 28-days posttreatment.Clinical Trial Registration-URL: http://www.clinicaltrials.gov. Unique identifier: NCT01393132. |
| PMID: 25826322 [PubMed - in process] | |
| Related citations | |
 |
| 5. | Postgrad Med. 2015 Mar 27:1-5. [Epub ahead of print]
Gokce G1, Hurmeric V, Mumcuoglu T, Ozge G, Basaran Y, Unal HU, Bolu E, Mutlu FM.
Author information:
Abstract
PURPOSE:
Idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (IHH) is an endocrine disorder defined with the presence of typical clinical signs and symptoms plus laboratory confirmation of serum testosterone (T) levels lower than 300 ng/dl. Androgen replacement therapy (ART) is the first-step treatment of male IHH. To date, no clinical trial, which investigates the changes on corneal structure and tear function, of systemic ART in men have been published. The objective of this study was to investigate the effects of ART on cornea and tear function in patients with IHH. MATERIALS AND METHODS:
This prospective, interventional study was conducted at the Gulhane Military Medical Academy, Ankara, Turkey, a tertiary referral military hospital. Thirty-four eyes of 17 men with IHH patients were evaluated with Schirmer I test, ultrasound pachymeter, applanation tonometer and confocal microscopy. A Testosterone compound (Sustanon® 250 mg) was administered by intramuscular injection in the course of a 3-week period to induce puberty, and human chorionic gonadotropin (Pregnyl® 5000 IU) was administered twice weekly for 3 months to induce fertility. The patients were re-evaluated at the third month of the treatment. Main Outcome Measures were Schirmer score, central corneal thickness (CCT), intraocular pressure (IOP), endothelial cell density, coefficient of variation and cell shape. RESULTS:
Schirmer scores showed similar results after the treatment compared to pre-treatment levels (p = 0.14). There was no statistically significant difference in CCT and IOP compared to baseline data (p = 0.96, p = 0.73, respectively), and no significant differences were found in corneal endothelial cell density, percentage of cell size variability or hexagonality (p = 0.83, p = 0.58, p = 0.64, respectively). CONCLUSIONS:
This is the first study that investigates the effects of ART on corneal structure and tear function in men. ART seems to have no short-term effects on corneal structure and tear function. Further publications of larger, long-term and controlled studies are needed. |
| PMID: 25812631 [PubMed - as supplied by publisher] | |
| Related citations | |
 |
| 6. | Exp Eye Res. 2015 Feb;131:77-83. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2015.01.005. Epub 2015 Jan 7.
Author information:
Abstract
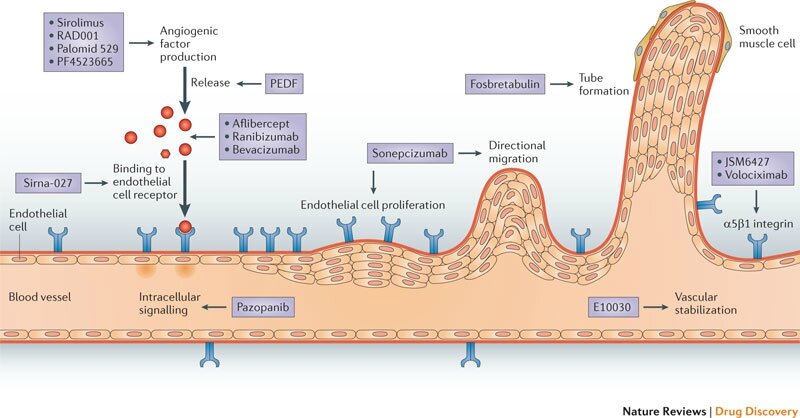
As a part of the visual cycle, all-trans-retinol (all-trans-ROL), the major form of vitamin A in circulating blood, is transported to the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE). All-trans-ROL is essential for normal retina function. However, recent researches have shown that excessive retinol intake can cause increase of all-trans-retinal. This can lead to the accumulation of lipofuscin, which is important in the pathogenesis of retina degeneration disease, such as dry type age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Since there are few reports regarding the involvement of all-trans-ROL in exudative AMD, we investigated the effects of all-trans-ROL in vitro and in vivo. We evaluated vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression in ARPE-19 cells and THP-1 cells after all-trans-ROL treatment using ELISA and real-time RT-PCR. In-vitro tube formation assay was performed with HUVEC cells using the conditioned medium (CM) obtained from ARPE-19 cells treated with all-trans-ROL. Transcriptional activity of retinoic acid receptor (RAR) was evaluated using luciferase assay. In mice, VEGF expressions were investigated in the retina and RPE/choroid after three weeks of excessive oral retinol intake. Laser-induced choroidal neovascularization (CNV) models were evaluated after they were fed with various doses of retinol. VEGF mRNA expression and VEGF production were significantly increased in all-trans-ROL treated ARPE-19 cells, which were inhibited by an RAR antagonist LE540. In contrast, there were no significant changes in VEGF production in THP-1 cells. Transcriptional activity of RAR was upregulated by all-trans-ROL treatment in ARPE-19 cells. The CM, obtained from ARPE-19 cells treated with all-trans-ROL, induced more capillary-like tube formation than cells treated with control vehicles. In vivo, the high retinol diet group has increased VEGF expression in the RPE/choroid and larger lesion size was induced. Our results suggest that all-trans-ROL is a pro-angiogenic factor. Excessive retinoid intake may be a potential risk factor for exudative AMD. Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. |
| PMID: 25576666 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE] | |
| Related citations | |
 |
| 7. | Optom Vis Sci. 2014 Dec;91(12):e301-4. doi: 10.1097/OPX.0000000000000405.
Author information:
Abstract
PURPOSE:
Behcet disease (BD) is a chronic, relapsing inflammatory disorder of unknown etiology characterized by obstructive vasculitis. Ocular surface involvement is a less frequent anterior segment finding. We report a patient with BD whose ocular presentation was severe surface involvement. CASE REPORT:
A 26-year-old Chinese woman, who was diagnosed as having BD by a dermatologist because of oral and genital ulceration and erythema nodosum in the upper extremities 1 month ago, presented with dry eye syndrome, corneal ulceration, and conjunctival lesions. Both clinical and confocal microscope examination revealed bilateral severe inflammatory ocular surface disease. However, she did not have the common clinical ocular manifestations such as iridocyclitis, vitritis, retinal perivasculitis, or retinitis for BD. In addition to oral methylprednisolone and thalidomide, topical 1% prednisolone acetate ophthalmic suspension, tacrolimus ophthalmic suspension, and artificial tears were used. We observed for the first time histopathological changes of the eyelid in BD by confocal microscopy. CONCLUSIONS:
Ocular surface lesions should be noted as an uncommon but possible manifestation of BD. Such severe ocular surface lesions without uveitis require a thorough medical history, dermatological examination, and serological testing to arrive at a diagnosis of BD. Accordingly, routine examination of the ocular surface is recommended in patients with BD, and BD should be included in a list of differential diagnoses for patients with ocular surface lesions. |
| PMID: 25279778 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE] | |
| Related citations | |
 |
| 8. | J Cataract Refract Surg. 2014 Oct;40(10):1736-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2014.08.020.
Ribeiro GC1, Krueger RR2.
Author information:
Abstract
We describe the case of a 50-year-old woman with anterior basement membrane dystrophy and dry eyes who had femtosecond laser in situ keratomileusis (LASIK) with gas-bubble breakthrough during flap creation in both eyes. The gas-bubble breakthrough appeared beneath the applanation interface in advance of the leading laser edge in the right eye and behind the advancing laser edge in the left eye. The surgery was aborted and 5 days later, photorefractive keratectomy with mitomycin-C was performed in the right eye and LASIK in the left eye. When a gas-bubble breakthrough extends in front of the advancing laser edge of the flap, the surgery should be aborted; surface ablation can be performed as a second-stage procedure. However, if the breakthrough occurs behind the advancing laser edge, the flap can be carefully lifted and the LASIK completed. FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE:
Dr. Krueger is a consultant to Alcon Laboratories, Inc. Dr. Ribeiro has no financial or proprietary interest in any material or method mentioned. Copyright © 2014 ASCRS and ESCRS. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. |
| PMID: 25263044 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE] | |
| Related citations | |
 |
| 9. | Cont Lens Anterior Eye. 2014 Aug;37(4):285-91. doi: 10.1016/j.clae.2014.03.002. Epub 2014 Apr 5.
Hickson-Curran S1, Spyridon M2, Hunt C2, Young G3.
Author information:
Abstract
PURPOSE:
Replacing soft contact lenses (CLs) on a daily basis brings a number of advantages, most notably, reduced exposure to deposits, disinfectants, allergens, and other contaminants. This retrospective study estimated the prevalence of problems in current wearers of reusable soft CLs and tested the effect of refitting "problem" patients with daily disposable (DD) hydrogel lenses. METHODS:
Prevalence was estimated from 398 current reusable CL wearers for: frequent/constant discomfort or dryness, ≥2 h of uncomfortable wear, ≥grade 2 conjunctival hyperaemia (0-4), or ≥grade 3 corneal staining (0-15). In the second part of the study, 217 reusable CL wearers classified as problem patients were randomly refitted with DD lenses manufactured from one of two materials: etafilcon A (n=96) or nelfilcon A (n=121) and reassessed 1 week later. RESULTS:
Thirty-nine percent (154/398) had some qualifying criterion: reduced comfortable wearing time (CWT), 20%; dryness, 20%; irritation, 5%; corneal staining, 8%; and hyperaemia, 7%. After refitting with DDs, the prevalence of reduced CWT was decreased from 65% to 51% (P=0.0039), dryness from 60% to 41% (P < 0.0001) and corneal staining from 28% to 21% (P=0.04). There was no significant change in the prevalence of irritation, or hyperaemia. Some differences were noted between the two lens materials. CONCLUSIONS:
A high proportion of reusable soft lens wearers encounter clinically relevant signs or symptoms with their current CLs. This study provides evidence that refitting with DD lenses is a useful strategy for alleviating some of the common problems of CL wear. Copyright © 2014 British Contact Lens Association. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. |
| PMID: 24709223 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE] | |
| Related citations | |
 |
| 10. | Clin Rheumatol. 2014 Aug;33(8):1189-93. doi: 10.1007/s10067-013-2480-3. Epub 2014 Jan 7.
Author information:
Abstract
We present a case report of a patient with Sjögren's syndrome accompanied with interstitial cystitis. A 64-year-old woman complained of dry mouth for 21 years, recurrent swelling and pain on the right parotid in 2000, and urinary irritation symptoms in the past 2 years. Several courses of different types of antibiotics could not relieve her urinary irritation symptoms. Bladder hydraulic dilatation had only transient effects. Urine sediment contained neither erythrocytes nor leukocytes, and urine cultures yielded no growth. However, increased γ-globulin, positive antinuclear antibodies, and anti-SS-A and anti-SS-B antibodies were detected. Histopathological data of labial salivary glands showed three foci of numerous mononuclear cells. Cystoscopy revealed redness, edema, angiectasis, and extensive ecchymosis of the mucosal surface and several small floating cruor entities in the bladder. Urinary bladder biopsy specimens revealed the absence of urothelium and edematous lamina propria and submucosa, with diffuse or multiple focal chronic inflammatory cell infiltration. Based on these findings, she was diagnosed with Sjögren's syndrome accompanied with interstitial cystitis. Therapy with corticosteroids relieved the symptoms significantly. |
| PMID: 24395198 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE] | |
| Related citations | |
 |
| 11. | Cont Lens Anterior Eye. 2014 Aug;37(4):257-61. doi: 10.1016/j.clae.2013.11.011. Epub 2013 Dec 19.
Author information:
Abstract
INTRODUCTION:
The Schirmer test (ST) evaluates the volume of tears in potential dry eye candidates via a strip placed in the lower tear lake. Previously reported inconsistencies in the results may be in part due to the lack of standardization as to the methodology, e.g. the eye position during the test. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of eye position on the ST score. METHODS:
. A ST was performed in a randomized fashion with and without anesthesia in three open eye positions (primary, superior and inferior) at 20° from each other. Palpebral aperture, age and a dry eye questionnaire (OSDI) were evaluated for correlation with the ST. RESULTS:
In the 20 non-dry eye volunteers (n=20, ages 18-40, mean OSDI score 10.5), the ST results were, as expected, lower overall (p < .001) with anesthesia (11.33 ± 7.78 mm) than without (19.74 ± 2.83 mm). The inferior gaze position resulted in higher values (p < .03) than the other two positions, regardless of the use of anesthesia. No correlation was noted between the palpebral aperture, age, questionnaire and the ST. CONCLUSION:
The ST seems to be influenced by the position of gaze. However, the mechanism for this, effect remains unclear. Further studies could focus on whether an inferior gaze of 20° compresses the tear film falsely, thereby elevating the tear volume. It is recommended that the clinician should adopt a standard eye position for the ST and that future reports provide specifics as to the methodology used. Copyright © 2013 British Contact Lens Association. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. |
| PMID: 24361097 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE] | |
| Related citations | |
 |
| 12. | Facial Plast Surg. 2013 Aug;29(4):281-8. doi: 10.1055/s-0033-1349362. Epub 2013 Jul 24.
Author information:
Abstract
This article provides a comprehensive discussion on the complications of blepharoplasty. We discuss the importance of preoperative counselling and surgical planning to provide the patient with a satisfactory outcome. Strategies are presented to manage common complications. Thieme Medical Publishers 333 Seventh Avenue, New York, NY 10001, USA. |
| PMID: 23884849 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE] | |
| Related citations | |
 |


/http%3A%2F%2Fstorage.canalblog.com%2F71%2F95%2F1309572%2F108183439_o.jpg)
/http%3A%2F%2Fstorage.canalblog.com%2F76%2F77%2F1309572%2F107960382_o.jpg)
/http%3A%2F%2Fstorage.canalblog.com%2F58%2F96%2F1309572%2F107815430_o.gif)
/http%3A%2F%2Fstorage.canalblog.com%2F12%2F26%2F1309572%2F107805770_o.jpg)