NEW PUBLICATIONS UPTO AUG. 31ST 2015 ON DRY EYE DIAGNOSIS AND THERAPEUTICS
NEW PUBLICATIONS UPTO AUG. 31ST 2015 ON DRY EYE DIAGNOSIS AND THERAPEUTICS
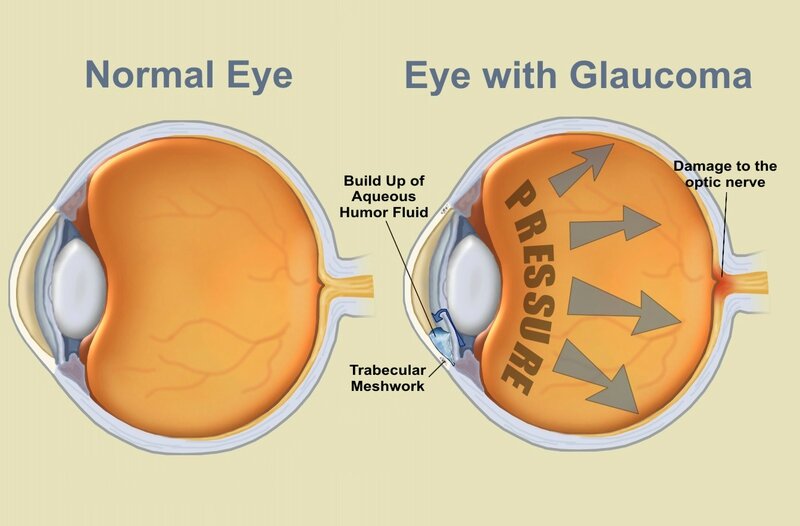
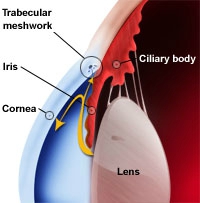
How chronic glaucoma treatment can give rise to ocular surface disease, and how you can treat them both. Mark B. Abelson, MD, CM, FRCSC, FARVO, and Ashley Lafond, Andover, Mass. 10/4/2011 As our patients age, an increased interest and heightened awareness of the changes occurring on the ocular surface is necessary.
http://www.reviewofophthalmology.com
| 1. | Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2015 Aug 27. [Epub ahead of print]
Author information:
Abstract
PURPOSE:
To evaluate the clinical efficacy of 3 % diquafosol sodium ophthalmic solution for dry eye, and to analyze the concentration of tear proteins and mucin-like substances after the treatment. METHODS:
Fifty eyes of 25 patients with dry eye syndrome were prospectively enrolled. The patients were treated with diquafosol solution at a dose of 1 drop in each eye 6 times daily for 4 weeks. The parameters of clinical efficacy were tear osmolarity, tear breakup time (BUT), fluorescein staining scores for the cornea and conjunctiva, Schirmer test values, and subjective symptoms evaluated using the ocular surface disease index (OSDI). Tears collected with Schirmer test strips were analyzed by high-performance liquid chromatography, and the concentrations of the total protein and the 4 major tear proteins, namely, secretory IgA, lactoferrin, lipocalin-1, lysozyme, and N-acetyl-neuraminic acid (Neu5Ac), were measured. Neu5Ac is a major sialic acid, a marker of secretory mucins. RESULTS:
The BUT, keratoconjunctival staining scores, and Schirmer test values were improved with statistical significance after the treatment with diquafosol solution, while changes in the other parameters, including tear osmolarity, corneal staining scores, and OSDI scores were not significant. The Neu5Ac concentration was significantly increased, which was not accompanied by changes in tear proteins. CONCLUSIONS:
Topical application of diquafosol significantly improved the clinical parameters of the BUT, keratoconjunctival staining scores, and Schirmer test values and was accompanied by increased sialic acid content in the tears of patients with dry eye. |
| PMID: 26310103 [PubMed - as supplied by publisher] | |
| Similar articles | |
 |
| 2. | Vestn Oftalmol. 2015 May-Jun;131(3):22-6.
[Article in Russian]
Boyko EV, Simakova IL, Yakushev DY, Ignat'Ev SA, Alekseev IB, Mel'Nikova NV, Alyab'Ev MV, Mal'Tsev DS.
Abstract
AIM:
to determine the frequency and severity of dry eye syndrome (DES) in primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG) patients that are newly diagnosed or already receiving beta blocker instillation therapy. MATERIAL AND METHODS:
A total of 127 patients (190 eyes) with POAG were divided into two groups. Group 1 included 55 newly diagnosed patients (88 eyes), group 2-72 POAG patients (102 eyes) instilling timolol 0.5% twice daily into the affected eye. The control group included 20 patients (40 eyes) aged 60-88 years (73.6 ± 9.2 years on average) with early age-related cataract. RESULTS:
DES was found in 69 POAG patients (79%) who was just starting their topical hypotensive therapy and 85 of those (84%) under treatment (p = 0.39). CONCLUSIONS:
One should take into account when prescribing ocular hypotensive therapy that newly diagnosed POAG patients usually already suffer from a dry eye. The use of topical beta blockers that contain preservatives exacerbates dry eye signs and symptoms in these patients. |
| PMID: 26310003 [PubMed - in process] | |
| Similar articles | |
| 3. | PLoS One. 2015 Aug 24;10(8):e0135629. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0135629. eCollection 2015.
Dienes L1, Kiss HJ1, Perényi K1, Szepessy Z1 , Nagy ZZ1, Barsi Á2, Acosta MC3, Gallar J3, Kovács I1.
Author information:
Abstract
PURPOSE:
To investigate the characteristics of ocular surface sensations and corneal sensitivity during the interblink interval before and after tear supplementation in dry eye patients. METHODS:
Twenty subjects (41.88±14.37 years) with dry eye symptoms were included in the dry eye group. Fourteen subjects (39.13±11.27 years) without any clinical signs and/or symptoms of dry eye were included in the control group. Tear film dynamics was assessed by non-invasive tear film breakup time (NI-BUT) in parallel with continuous recordings of ocular sensations during forced blinking. Corneal sensitivity to selective stimulation of corneal mechano-, cold and chemical receptors was assessed using a gas esthesiometer. All the measurements were made before and 5 min after saline and hydroxypropyl-guar (HP-guar) drops. RESULTS:
In dry eye patients the intensity of irritation increased rapidly after the last blink during forced blinking, while in controls there was no alteration in the intensity during the first 10 sec followed by an exponential increase. Irritation scores were significantly higher in dry eye patients throughout the entire interblink interval compared to controls (p<0.004). NI-BUT significantly increased after HP-guar (p = 0.003) but not after saline drops (p = 0.14). In both groups, either after saline or HP-guar the shape of symptom intensity curves remained the same with significantly lower irritation scores (p<0.004), however after HP-guar the decrease was significantly more pronounced (p<0.004). Corneal sensitivity to selective mechanical, cold and chemical stimulation decreased significantly in both groups after HP-guar (p<0.05), but not after saline drops (p>0.05). CONCLUSION:
Ocular surface irritation responses due to tear film drying are considerably increased in dry eye patients compared to normal subjects. Although tear supplementation improves the protective tear film layer, and thus reduce unpleasant sensory responses, the rapid rise in discomfort is still maintained and might be responsible for the remaining complaints of dry eye patients despite the treatment. |
| PMID: 26302222 [PubMed - in process] | |
| Similar articles | |
 |
| 4. | BMC Res Notes. 2015 Aug 23;8(1):368. doi: 10.1186/s13104-015-1367-6.
Renard D1, Rubli E2, Voide N3, Borruat FX4, Rothuizen LE5.
Author information:
Abstract
BACKGROUND:
Digoxin intoxication results in predominantly digestive, cardiac and neurological symptoms. This case is outstanding in that the intoxication occurred in a nonagenarian and induced severe, extensively documented visual symptoms as well as dysphagia and proprioceptive illusions. Moreover, it went undiagnosed for a whole month despite close medical follow-up, illustrating the difficulty in recognizing drug-induced effects in a polymorbid patient. CASE PRESENTATION:
Digoxin 0.25 mg qd for atrial fibrillation was prescribed to a 91-year-old woman with an estimated creatinine clearance of 18 ml/min. Over the following 2-3 weeks she developed nausea, vomiting and dysphagia, snowy and blurry vision, photopsia, dyschromatopsia, aggravated pre-existing formed visual hallucinations and proprioceptive illusions. She saw her family doctor twice and visited the eye clinic once until, 1 month after starting digoxin, she was admitted to the emergency room. Intoxication was confirmed by a serum digoxin level of 5.7 ng/ml (reference range 0.8-2 ng/ml). After stopping digoxin, general symptoms resolved in a few days, but visual complaints persisted. Examination by the ophthalmologist revealed decreased visual acuity in both eyes, 4/10 in the right eye (OD) and 5/10 in the left eye (OS), decreased color vision as demonstrated by a score of 1/13 in both eyes (OU) on Ishihara pseudoisochromatic plates, OS cataract, and dry age-related macular degeneration (ARMD). Computerized static perimetry showed non-specific diffuse alterations suggestive of either bilateral retinopathy or optic neuropathy. Full-field electroretinography (ERG) disclosed moderate diffuse rod and cone dysfunction and multifocal ERG revealed central loss of function OU. Visual symptoms progressively improved over the next 2 months, but multifocal ERG did not. The patient was finally discharged home after a 5 week hospital stay. CONCLUSION:
This case is a reminder of a complication of digoxin treatment to be considered by any treating physician. If digoxin is prescribed in a vulnerable patient, close monitoring is mandatory. In general, when facing a new health problem in a polymorbid patient, it is crucial to elicit a complete history, with all recent drug changes and detailed complaints, and to include a drug adverse reaction in the differential diagnosis. |
| PMID: 26298392 [PubMed - in process] | |
| Similar articles | |
  |
| 5. | Community Dent Health. 2015 Mar;32(1):5-7. |
| PMID: 26263585 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE] | |
| Similar articles | |
| 6. | Chin J Dent Res. 2015 Jun;18(2):95-101.
Abstract
OBJECTIVE:
To investigate the effects of the multi-glycosides of Tripterygium wilfordii (GTW) on Sjögren's syndrome (SS) in the non-obese diabetic (NOD) mouse model. METHODS:
Twenty-seven 8-week-old, female NOD mice were divided into the GTW group, the hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) group, and control (normal saline) group, and received corresponding treatment for 16 weeks. The treatment-induced changes in stimulated total saliva flow rate (STFR), level of serum anti-SSA/SSB, ratio of regulatory T (Treg) cells, histology of the submandibular gland (SMG) and the gene expression profile that is related to inflammation and autoimmunization were evaluated. RESULTS:
Compared to the untreated (control) mice, STRF, SMG index and Treg/CD4+ cell ratio were significantly higher, whereas anti-SSA, anti-SSB and lymphoid foci were remarkably lower in GTW-treated mice. HCQ-treated mice showed similar results except SMG index was not different from the untreated mice. NOD mice showed 19.03% altered gene expression with maturation from the age of 8 weeks to 24 weeks. Treatment with HCQ and GTW reduced the change in gene expression to 13.09% and 7.14%, respectively. CONCLUSION:
GTW is as effective as HCQ in the treatment of Sjögren's syndrome in the NOD mouse model. |
| PMID: 26167547 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE] | |
| Similar articles | |
| 7. | Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2015 Jul;26(4):319-24. doi: 10.1097/ICU.0000000000000171.
Author information:
Abstract
PURPOSE OF REVIEW:
Dry eye syndrome can be difficult to manage in severe or refractory cases. In patients in whom traditional treatments have limited efficacy, alternative treatments may be considered for dry eye syndrome, including scleral lenses. The present review summarizes the evidence regarding scleral lens use in dry eye syndrome. RECENT FINDINGS:
Scleral lenses have become a viable option for severe dry eye syndrome, and have been shown to be efficacious and well tolerated, with most reports citing improved visual acuity and relief of symptoms. Currently, there are 18 manufacturers of scleral lenses, although published reports on scleral lenses primarily focus on the BostonSight PROSE and the Jupiter Lens. SUMMARY:
Scleral lenses are efficacious and well tolerated for use in severe dry eye syndrome. Further research is needed to compare different sizes and types of lenses, and to standardize outcome measures. |
| PMID: 26058032 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE] | |
| Similar articles | |
 |
| 8. | Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2015 Jul;26(4):260-4. doi: 10.1097/ICU.0000000000000158.
Author information:
Abstract
PURPOSE OF REVIEW:
Small-incision lenticule extraction (SMILE) is a novel technique devised to correct refractive errors. SMILE circumvents excimer laser photoablation of cornea, as the stromal lenticule cut by femtosecond laser is removed manually. Smaller incisions and preservation of anterior corneal biomechanical strength have been suggested as some of the advantages of SMILE over femtosecond laser-assisted LASIK (FS-LASIK). In this review, we compared previous published results of SMILE and FS-LASIK. The advantage, efficacy and safety of SMILE are compared with FS-LASIK. RECENT FINDINGS:
SMILE achieved similar efficacy, predictability and safety as FS-LASIK. Greater preservations of corneal biomechanical strength and corneal nerves were observed in SMILE when compared with LASIK or PRK. Additionally, the incidence of postoperative dry eye syndrome was found to be less problematic in SMILE than in FS-LASIK. SUMMARY:
SMILE is a promising new surgery for refractive error correction. Prospective and retrospective studies of SMILE have shown that results of SMILE are similar to FS-LASIK. With advances in femtosecond laser technology, SMILE may gain greater acceptance in the future. |
| PMID: 26058022 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE] | |
| Similar articles | |
 |
| 9. | Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2015 Jul;26(4):243-8. doi: 10.1097/ICU.0000000000000173.
Author information:
Abstract
PURPOSE OF REVIEW:
The last two decades have brought advances in materials and manufacturing of large diameter rigid gas-permeable contact lenses, and a greater appreciation of the role of scleral lenses for therapeutic indications. The purpose of this review is to provide an update on the use of rigid gas-permeable scleral lenses in the management of patients with complications after refractive surgery. RECENT FINDINGS:
There are recent reports on clinical experience with specific scleral lens designs from single institutions in cohorts that include patients who have undergone refractive surgery. Typically, these are patients with 'irregular corneas' after radial keratotomy or LASER assisted in-situ keratomileusis, but patients with keratectasia, dry eye syndrome, and corneal neuralgia are also reported. Visual outcomes and wearing success rates are high in these reports, although outcomes for refractive surgery patients are not reported separately. SUMMARY:
Clinicians who encounter patients with complications after corneal refractive surgery should be aware of advances in scleral lenses. Scleral lenses are an alternative to surgical intervention in patients who might otherwise be considered poor contact lens candidates. |
| PMID: 26058019 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE] | |
| Similar articles | |
 |
| 10. | Autoimmun Rev. 2015 Aug;14(8):742-50. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2015.04.009. Epub 2015 Apr 24.
Guellec D1, Cornec-Le Gall E2, Groh M3, Hachulla E4, Karras A5, Charles P6, Dunogué B3, Abad S7, Alvarez F8, Gérard F1, Devauchelle-Pensec V9, Pers JO10, Puéchal X3, Guillevin L3, Saraux A9, Cornec D11; CRI (Club Rhumatismes et Inflammation) and the French Vasculitis Study Group.
Author information:
Abstract
OBJECTIVES:
To describe the clinical presentation, management and prognosis of patients diagnosed with both primary Sjögren's syndrome (pSS) and anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis (AAV). METHODS:
French nation-wide survey completed by a systematic literature review. RESULTS:
This work identified 7 new cases of coexisting pSS and AAV: 2 microscopic polyangiitis (MPA), 2 granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA), 2 anti-myeloperoxidase (MPO)-ANCA renal-limited AAV, and 1 eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA). The systematic literature search identified 15 previously published cases. Among the 22 patients, 19 were females. Mean age at diagnosis of AAV was 63.9±9.8years. All individuals with available information experienced at least one extra-glandular manifestation attributable to pSS. p-ANCA with anti-MPO specificity were found in 76.2% (16/21), c-ANCA with anti-PR3 specificity in 14.3% (3/21) and isolated c-ANCA in 13.6% (3/22). Vasculitis involved kidneys (n=13), lungs (n=8), skin (n=6), peripheral nerves (n=5), central nervous system (n=2), small bowel (n=1), muscle (n=1), ear chondritis (n=1) and sinuses (n=1). The mean AAV follow-up was 73.5 (±120.0) months. While on treatment, disease remission occurred in 77.3% of cases, and one death was reported in the first 6months after diagnosis. CONCLUSION:
This work shows that AAV may occur in patients with pSS. These are most commonly p-ANCA associated vasculitis with anti-MPO specificity. AAV may reveal an underlying pSS or arise during its evolution, but did not precede pSS in any of these cases. AAV occurrence appears to be correlated with extra-glandular manifestations of pSS. Copyright © 2015 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved. |
| PMID: 25916811 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE] | |
| Similar articles | |
 |
| 11. | Lupus. 2015 Jan;24(1):94-7. doi: 10.1177/0961203314554848. Epub 2014 Oct 8.
Conti F1, Spinelli FR2, Colafrancesco S2, Truglia S2, Ceccarelli F2, Fattapposta F3, Sorice M4, Capozzi A4, Ferretti G5, Priori R2, Martinelli F2, Pirone C2, Alessandri C2, Valesini G2.
Author information:
Abstract
Central nervous system (CNS) involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is reported in about 50% of patients. Among the neuropsychiatric features of SLE, myelopathy, including acute transverse myelitis (ATM) or acute longitudinal myelitis (ALM), represents an uncommon event. A possible vascular aetiology of SLE myelopathies has been hypothesized and it seems to be much more associated to SLE-associated antiphospholipid syndrome (APS). Furthermore, a possible infectious cause of ATM or ALM in healthy subjects has been described. SLE patients are susceptible to infection due to the disease itself or to the immunosuppressive therapy. Cryptococci non-neoformans have been rarely associated to infections in humans. Here we describe the case of a 47-year-old woman with SLE and Sjögren Syndrome who developed an ALM concurrently with a Cryptococcus laurentii pneumonia. The patient was treated with antimycotics, high doses of glucocorticoids and intravenous immunoglobulins with a significant clinical and radiological improvement. As far as we know, this is the first case of Cryptococcus laurentii infection and ALM in a patient with SLE who later developed a seronegative APS. Even though myelopathy may be considered primarily associated to SLE, a possible role of the infection in ALM development cannot be excluded. © The Author(s) 2014 Reprints and permissions: sagepub.co.uk/journalsPermissions.nav. |
| PMID: 25297553 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE] | |
| Similar articles | |



/http%3A%2F%2Fstorage.canalblog.com%2F71%2F95%2F1309572%2F108183439_o.jpg)
/http%3A%2F%2Fstorage.canalblog.com%2F76%2F77%2F1309572%2F107960382_o.jpg)
/http%3A%2F%2Fstorage.canalblog.com%2F58%2F96%2F1309572%2F107815430_o.gif)
/http%3A%2F%2Fstorage.canalblog.com%2F12%2F26%2F1309572%2F107805770_o.jpg)