Publications ending March 27 th 2015
LINK LOWER EYE LID: cet_15_06_2012_reuser
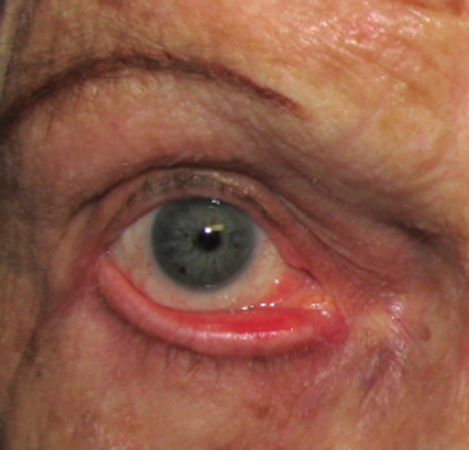
Patient#1 (Preoperative). This patient complained of eyelids that were low and interfering with vision, as well as giving her a tired appearance.
Patient#1 (Postoperative, 3 months). After bilateral upper lid lift (ptosis repair), external blepharoplasty of the upper lids, and external blepharoplasty of the lower lids.
Thanks to J. Walrath website: http://josephwalrathmd.com/results/reconstruction-prepost/
| 2. | J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2015 Mar 24. pii: jpet.114.222414. [Epub ahead of print]
Author information:
Abstract
Treatment for fibromyalgia is an unmet medical need. To develop novel therapies for the treatment of fibromyalgia, we explored pain therapeutic actions of existing pharmaceuticals, which inhibit the somatic symptoms frequently observed in fibromyalgia patients. The present study first examined the therapeutic actions of pilocarpine, which inhibits dry-eye and dry-mouth symptoms, using an experimental fibromyalgia-like chronic pain model produced by intermittent cold stress (ICS) in mice. A single intraperitoneal (i.p.) and intracerebroventricular (i.c.v.), but not intrathecal, pilocarpine administration attenuated ICS-induced thermal hyperalgesia and mechanical allodynia, and this action was abolished by muscarinic antagonist pirenzepine (i.c.v.). Treatment with 1-10 μg/kg donepezil (i.p.), which can easily penetrate into the brain, also showed similar therapeutic effects. Importantly, we found that both of pilocarpine and donepezil produced anti-hyperalgesic effects via supraspinal action. Furthermore, repeated donepezil treatments completely cured the ICS-induced hyperalgesia and allodynia even after the cessation of drug treatments. Acute and chronic treatments of these cholinomimetics had no effects on the nociceptive threshold in control animals. In contrast, the lack of morphine (i.c.v.) analgesia initially observed in the ICS model remained in ICS model mice treated with long-term donepezil. Collectively, these findings suggest that stimulation of the muscarinic cholinergic system effectively inhibits some mechanisms underlying chronic pain in the ICS model, but not the lack of descending pain inhibitory mechanisms, which is driven by central morphine. The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. |
| PMID: 25805256 [PubMed - as supplied by publisher] | |
| Related citations | |
| 3. | Curr Eye Res. 2015 Mar 24:1-6. [Epub ahead of print]
Author information:
Abstract
PURPOSE:
To compare the responses to dry eye treatment of patients sorted by the degree of lower lid laxity. METHODS:
Sixty patients were grouped into three groups according to the degree of lower lid laxity. Tear break-up time (TBUT), Schirmer test (ST) scores, ocular surface disease index (OSDI) scores, and changes in OSDI score in each group were compared, before and at 3 months after treatment. RESULTS:
TBUT, ST, and OSDI scores were not different among the three groups at baseline. TBUT improved in each group at 3 months after treatment, and no differences between groups were found. ST scores were not increased after treatment, while OSDI were improved to 22.57 ± 5.243, 31.16 ± 11.353, and 37.85 ± 13.342 in the no, moderate, and high laxity groups, respectively; these improvements were statistically significant (p = 0.003, <0.001, <0.001, respectively). Patients with greater than moderate lower lid laxity saw the smallest improvement in response to dry eye treatment, as assessed by change in OSDI score (p = 0.005 versus moderate laxity group, p = 0.005 versus no laxity group). CONCLUSIONS:
Lower lid laxity is one of the factors contributing to the responses to dry eye treatment assessed by change in OSDI score, independent of TBUT and ST scores. |
| PMID: 25802947 [PubMed - as supplied by publisher] | |
| Related citations | |
 |
| 4. | Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:527926. doi: 10.1155/2015/527926. Epub 2015 Feb 23.
Villatoro AJ1, Fernández V1, Claros S2, Rico-Llanos GA3, Becerra J3, Andrades JA2.
Author information:
Abstract
Keratoconjunctivitis sicca (KCS) or dry eye disease (DED) is an immune-mediated multifactorial disease, with high level of prevalence in humans and dogs. Our aim in this study was to investigate the therapeutic effects of allogeneic adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells (Ad-MSCs) implanted around the lacrimal glands in 12 dogs (24 eyes) with KCS, which is refractory to current available treatments. Schirmer tear test (STT) and ocular surface integrity were assessed at 0 (before treatment), 3, 6, and 9 months after treatment. Average STT values and all clinical signs showed a statistically significant change (P < 0.001) during the follow-up with reduction in all ocular parameters scored: ocular discharge, conjunctival hyperaemia, and corneal changes, and there were no signs of regression or worsening. Implanted cells were well tolerated and were effective reducing clinical signs of KCS with a sustained effect during the study period. None of the animals showed systemic or local complications during the study. To our knowledge, this is the first time in literature that implantation of allogeneic Ad-MSCs around lacrimal glands has been found as an effective therapeutic alternative to treat dogs with KCS. These results could reinforce a good effective solution to be extrapolated to future studies in human. |
| PMID: 25802852 [PubMed - in process] | |
| Related citations | |
  |
| 5. | Rheumatology (Oxford). 2015 Feb;54(2):219-30. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keu417. Epub 2014 Oct 22.
Sada PR1, Isenberg D1, Ciurtin C2.
Author information:
Abstract
SS is a chronic systemic autoimmune disease characterized by decreased exocrine gland function. A variety of other disease manifestations may also be present, including general constitutional symptoms and extraglandular features. A multidisciplinary approach focused on both local and systemic medical therapies is needed as the disease has a wide clinical spectrum. The current treatment for SS is mainly symptomatic. However, there is evidence that systemic drugs are effective in controlling extraglandular manifestations of the disease. Overall evidence for the role of conventional immunosuppressive therapy is limited. A number of attempts to use biologic therapies have led to variable results. Biologic agents targeting B cells, such as rituximab, epratuzumab and belimumab, have shown promising results, but further studies are needed to validate the findings. Early-phase studies with abatacept and alefacept proved that T cell stimulation inhibition is another potentially effective target for SS treatment. Modulation or inhibition of other targets such as IFN, IL-6 and Toll-like receptor are also currently being investigated. We have summarized the available evidence regarding the efficacy of biologic treatments and discuss other potential therapies targeting pathways or molecules recognized as being involved in the pathogenesis of SS. © The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Rheumatology. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com. |
| PMID: 25342375 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE] | |
| Related citations | |
| 6. | Br J Haematol. 2015 Feb;168(3):317-27. doi: 10.1111/bjh.13192. Epub 2014 Oct 15.
Author information:
Abstract
Primary Sjögren Syndrome (pSS) is an autoimmune disease associated with an increased risk of lymphoma. Lymphomas complicating pSS are mostly low-grade B cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas, predominantly of marginal zone histological type. Mucosal localization is predominant, notably mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphomas. Lymphomas often develop in organs where pSS is active, such as salivary glands. Germinal centre (GC)-like structures, high TNFSF13B (BAFF) and Flt3-ligand (FLT3LG) levels and genetic impairment of TNFAIP3 are new predictors of lymphoma development. These new findings allow a better understanding of the pathogenic mechanisms leading to lymphoma. We propose the following scenario: auto-immune B cells with rheumatoid factor (RF) activity are continuously stimulated by immune complexes containing antibodies against more specific auto-antigens, such as SSA/Ro, SSB/La or others. Germline abnormality of TNFAIP3 leads to a decreased control of the NF-kB pathway and thus promotes survival of B cells and oncogenic mutations especially in GC structure. Moreover, B cells are stimulated by a positive loop of activation induced by BAFF secretion. Thus, lymphomagenesis associated with pSS exemplifies the development of antigen-driven B-cell lymphoma. The control of disease activity by a well-targeted immunosuppressor is the primary objective of the management of the patient in order to repress chronic B cell stimulation. © 2014 John Wiley & Sons Ltd. |
| PMID: 25316606 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE] | |
| Related citations | |
 |
| 7. | Rheumatology (Oxford). 2015 Jan;54(1):163-8. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keu292. Epub 2014 Jul 26.
Alunno A1, Montanucci P1, Bistoni O1, Basta G1, Caterbi S1, Pescara T1, Pennoni I1, Bini V1, Bartoloni E1, Gerli R2, Calafiore R1.
Author information:
Abstract
OBJECTIVE:
Human umbilical cord Wharton jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells (hUCMS) are easy to retrieve in bulk. They may interact with immune cells by either cell contact or soluble factors. Little evidence is currently available on potential therapeutic application of hUCMS to systemic autoimmune disorders such as primary SS (pSS). We have recently developed an endotoxin-free alginate gel that can be used to microencapsulate different cell types for graft into non-immunosuppressed hosts. We aimed to assess the in vitro effects of IFN-γ-pretreated microencapsulated (CpS)-hUCMS on T cells of pSS. METHODS:
Ten pSS patients and 10 healthy donors were selected. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were obtained from venous blood to establish co-cultures with CpS-hUCMS. Lymphocyte proliferation and phenotypic analysis was performed by flow cytometry and real-time PCR on IFN-γ-pretreated hUCMS was performed before PBMCs co-culture. RESULTS:
We found that CpS-hUCMS suppress pSS T cell proliferation and restore the Treg/Th17 ratio, thereby possibly positively impacting the pSS disease process. CONCLUSION:
We have developed a new biohybrid drug delivery system that now waits for clinical application in autoimmune diseases, including pSS. © The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Rheumatology. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com. |
| PMID: 25065014 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE] | |
| Related citations | |





/http%3A%2F%2Fstorage.canalblog.com%2F11%2F32%2F1309572%2F107152682_o.jpg)
/http%3A%2F%2Fstorage.canalblog.com%2F31%2F09%2F1309572%2F106985502_o.jpg)
/http%3A%2F%2Fstorage.canalblog.com%2F19%2F98%2F1309572%2F106687605_o.jpg)
/http%3A%2F%2Fstorage.canalblog.com%2F52%2F98%2F1309572%2F106438658_o.gif)